알고 팁들
- '\' 문자열 쓰는법
\'', \\ 를 쓴다.
- 16진수 : cout << hex << 변,상수;
- 소수 n번째 자리 까지
cout <<fixed;
cout.precision(n) : ex) n이 6이면 1235.677777
해제 : cout.unsetf(ios::fixed)
- call by reference
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
#include <iostream>
void swapp(int &a, int &b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int main()
{
int a,b;
swapp(a,b);
}
|
cs |
- 입출력 최적화
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
- 입력에서 특별한 EOF 처리가 없을때
1. while(cin >> a) 하면 마지막에 끝난다.
2. If(cin.eof() == true) 로 중간에 끊을 수 있다.
- iterator : <vector> 에서 위치 조정으로 사용한다.
- vector<int> a; => 초기 선언
- vector<int>::iterator itr = v.begin(); => 벡터 반복자 지정
- *itr => 현재 위치
- itr[3] => 4번째 위치 임의 접근
- itr += 2 => 2칸 이동
- for(itr = a.begin() ; itr != v.end() ; ++itr) => 처음부터 끝까지
cout << *itr << endl;
- 그외 : size(), a.swap(b), insert(itr,3), erase(itr), empty ……
- 근데 iterator보다는 [] 선언이 훨 편하다.
- pair
vector<pair<char, int>> p;
p.push_back(pair<char,int>(‘a’, b)); (O)
p.push_back(make_pair(‘a’,b)); (X) => pair가 Point같은 구조체에선 안된다.;
sort(p.begin(), p.end());
- int a = 9;
if ( a <= 9)
cout << “aa”
else if(a<=99)
cout << ”bb”
결과는??? : aa만 나온다 bb무시함.
- Arr[1000000](백만) 급 은 지역보다 전역에 넣어주자…
- 파이 사용하기
define과 include의 위치가 뒤바뀌면 안된다!!
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
#include <math.h>
int a = M_PI
- 에라토스테네스의 체 (easy)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[1001] = { 0 };
arr[1] = 1; // 0 은 소수, 1 은 소수가 아님
for (int i = 2; i <= 1000; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == 1)
continue;
for (int j = i*2; j <= 1000; j += i)
{
arr[j] = 1;
}
}
for (int i = 2; i <= 1000; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == 0)
cout << i << " ";
}
}
|
cs |
-정렬 #include <algorithm>
- Arr[5] = {3,5,4,2,1};
sort(a+2, a+5); -> 3번째부터 5번째까지이다. 마지막 주소라서 그럶
- 함수로 정렬을 custom 할 수 있다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool custom(const int& a, const int& b)
{
return a > b;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
int arr[6] = { 5,1,2,2,4,3 };
sort(arr, arr+6, custom);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
cout << arr[i];
}
|
cs |
- vector<int> a(100); => sort(a.begin(), a.end());
- Point 정렬
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public :
int x, y;
};
bool comp(const Point& p1, const Point& p2)
{
if (p1.x == p2.x)
return p1.y < p2.y;
else
return p1.x < p2.x;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
Point p[5];
p[0] = { 1,3 }; p[1] = { 4,3 }; p[2] = { 3,1 };
p[3] = { 5,5 }; p[4] = { 2,1 };
sort(p, p + 5, comp);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
cout << '[' << p[i].x << ' ' << p[i].y << ']';
}
|
cs |
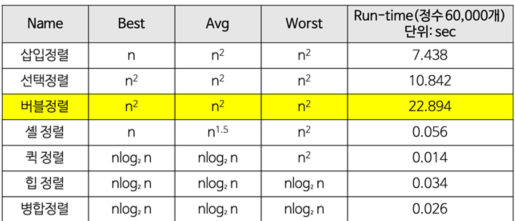
- String * str = new string[3];
str[0] = “ddd”
str[1] = “a”
str[2] = “ddd”
swap(str[1], str[2]) 가능. sort(str, str+a) 가능.
- bool("aaa" < "aab")의 리턴값은???? : 1이다.
- 문자열 입력에서 스페이스바를 포함한 한줄 싹 받기
#include <string>
main()
string str;
getline(cin, str) (getLine이 아니다.)
- taskkill
netstat -ano 후 kill 할 PID를 찾는다. -> taskkill /f /PID 1234
- 들여쓰기
#include <iomanip>
cout << setw(2) << i << ' ';
- string -> int : stoi("1231231");
- int -> string : to_string(123123);