복습이 필요한 알고 팁
정렬 STL을 잘 써보자
헐랭미
2020. 6. 26. 10:51
먼저 아주 일반적인 정렬을 커스텀하는 방법이다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool custom(const int& a, const int& b)
{
return a > b;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
int arr[6] = { 5,1,2,2,4,3 };
sort(arr, arr+6, custom);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
cout << arr[i];
}
|
cs |
- vector<int> a(100); => sort(a.begin(), a.end());
그리고 class 나 struct형에 대한 정렬 방법이다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public :
int x, y;
};
bool comp(const Point& p1, const Point& p2)
{
if (p1.x == p2.x)
return p1.y < p2.y;
else
return p1.x < p2.x;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
Point p[5];
p[0] = { 1,3 }; p[1] = { 4,3 }; p[2] = { 3,1 };
p[3] = { 5,5 }; p[4] = { 2,1 };
sort(p, p + 5, comp);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
cout << '[' << p[i].x << ' ' << p[i].y << ']';
}
|
cs |
이제 여기서 신경써야 하는것이 있다.
int arr[10], vector<int> 와 비교해서
set<int> , priority_queue<int> 의 특징은 무엇인가??? 수를 넣을 때 바로 정렬이 된다는 것이다.
이런 것은 이제 또 조금 다른 방식의 정렬방법을 취한다.
제일 큰 특징이라면 bool comp 에서 class comp -> bool operator() 로 바뀐다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#define pii pair<int, int>
using namespace std;
class comp
{
public :
bool operator() (const int& a, const int& b) const
{
return a > b;
}
};
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
int arr[13] = { 5,3,1,5,6,4,9,6,2,8,3,2,1 };
set<int, comp> s;
for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++)
s.insert(arr[i]);
set<int>::iterator itr = s.begin();
for (itr; itr != s.end(); itr++)
cout << *itr << ' ';
}
|
cs |
이번엔 Priority Queue를 보자.
PQ의 디폴트는 최대 힙이다.)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define pii pair<int, int>
using namespace std;
class comp
{
public:
bool operator() (const int& a, const int& b) const
{
return a < b;
}
};
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
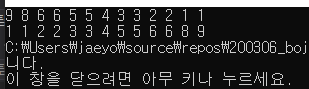
int arr[13] = { 5,3,1,5,6,4,9,6,2,8,3,2,1 };
// priority_queue<int> pq;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, comp> pq;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pqpq;
for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++)
{
pq.push(arr[i]);
pqpq.push(arr[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++)
{
cout << pq.top() << ' ';
pq.pop();
}
cout << '\n';
for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++)
{
cout << pqpq.top() << ' ';
pqpq.pop();
}
}
|
cs |